Rounding millilitres to ounces is a fundamental skill for pharmacy professionals, especially those preparing for the NAPLEX. Understanding how to accurately convert and round these measurements is essential for ensuring safe and effective medication administration.
This article will explore the vital techniques and considerations in calculating medication dosage, emphasizing the importance of rounding in pharmacy practices.
We will provide in-depth insights, practical tips, and examples to help you master this critical aspect of pharmaceutical calculations.
Grasping the Concept of Rounding mL in an oz NAPLEX 30
To effectively understand rounding millilitres to ounces, it’s essential to grasp the basic principles of volume measurement in pharmacy. Milliliters (mL) and ounces (oz) are standard units that express liquid volumes, particularly in medication administration.
The conversion factor is crucial here; 1 ounce equals approximately 29.5735 millilitres. Pharmacists often use the simplified approximation of 30 mL per ounce for many quick calculations. While this can streamline processes during busy shifts, precision is vital when dealing with medications.
Key Conversion Factors
- 1 ounce (oz) = 29.5735 milliliters (mL)
- 30 mL ≈ 1 oz (for quick calculations)
Understanding how to apply this conversion accurately can significantly improve your performance when preparing for the pharmacy board exam.
It would help if you practised these conversions regularly, as the ability to round millilitres to ounces efficiently is vital during patient care situations and exams.
The Importance of Rounding in Pharmacy Calculations
Rounding plays a critical role in maintaining dosing accuracy. In pharmacy, the general guideline is to round up if the decimal is 0.5 or higher and round down if it is lower. This rule is crucial for preventing potential errors that could compromise patient safety.
Rounding Rules to Follow:
- Round up if the decimal is 0.5 or greater.
- Round down if the decimal is less than 0.5.
Understanding these rules is not merely a matter of adhering to a procedure; it directly impacts clinical outcomes.
Incorrect rounding can lead to dosing errors that result in inadequate or excessive medication being administered, which can have severe consequences for patient health.
Ensuring Medication Dose Accuracy
Accurate medication dosing is paramount for safeguarding patient health and achieving effective treatment outcomes. Pharmacists must consider various patient-specific factors, such as age, weight, and medical history, to ensure the correct dose of medication is administered.
Factors Affecting Dosing Accuracy:
- Patient Age: Pediatric and geriatric populations often require more precise dosing due to their unique physiological responses to medications.
- Patient Weight: Body weight can significantly impact drug metabolism and efficacy.
- Medical Conditions: Coexisting medical conditions can alter a patient’s response to certain medications, necessitating careful dosing considerations.
Pharmacists must remain vigilant and thorough when calculating doses, as even minor variations can lead to adverse side effects or treatment failures.
Regularly reviewing dosing protocols for pharmacists can help reinforce the importance of accuracy and ensure that each medication dispensed aligns with best practices.
Balancing Manual Skills and Digital Tools in Pharmacy
While developing manual conversion skills is essential for pharmacy professionals, leveraging digital tools can significantly
improve efficiency in fast-paced environments. Many pharmacists utilize applications that facilitate quick conversions between millilitres (mL) and ounces (oz), streamlining their workflow.
Recommended Digital Tools:
- MedCalc
- PharmCalc
- Pillbox
However, it’s important to remember that digital devices are prohibited during the NAPLEX. Therefore, you must commit essential conversion factors to memory.
For example, knowing that 30 mL is roughly equivalent to 1 oz enables pharmacists to perform rapid mental conversions, which is beneficial during exams and everyday practice.
The Critical Nature of Accurate Dosage Conversions
Accurate dosage calculations are vital, especially when working with sensitive populations, such as children and the elderly. These groups often require precise dosing because their bodies metabolize medications differently.
Case Study: Pediatric Dosing
Consider a scenario where a pediatric medication is prescribed at 2.54 oz. If a pharmacist mistakenly rounds this to 2.5 oz instead of 2.6 oz, the child may not receive the therapeutic effect intended, potentially compromising their treatment.
While seemingly minor, such errors highlight the importance of precision, especially in vulnerable populations.
Pharmacists must adhere to established nursing dosage guidelines, and know-how measurement conversions in pharmacy can significantly affect clinical outcomes.
The Importance of Rounding in Medication Dosing
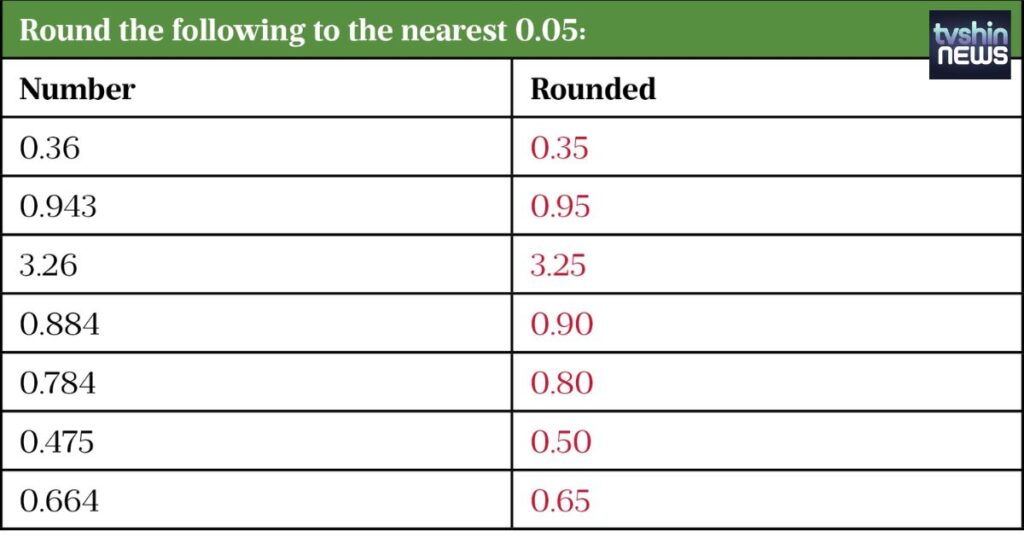
Rounding is crucial for ensuring accurate prescription dosing in pharmaceutical calculations. The precision of rounding techniques directly influences patient care and treatment outcomes.
Benefits of Standardized Rounding Practices:
- Enhances Communication: Consistent rounding minimizes confusion during the prescription filling and administration.
- Builds Trust: Patients rely on pharmacists to deliver medications accurately, and adherence to rounding protocols fosters confidence in therapy.
By understanding and applying these rounding techniques, pharmacists can mitigate the risks of overdosing or underdosing and maintain dosages within safe and effective ranges.
Avoiding Common Errors in Unit Conversions
Errors in unit conversions often stem from premature rounding or misremembering conversion factors. To achieve optimal precision, complete the entire calculation before applying any rounding, saving this step for the final stages.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Rounding too early: Ensure that all calculations are finished before rounding.
- Misremembering conversion factors: Always verify that you have the exact figure of 29.5735 mL for 1 oz in mind during conversions.
By maintaining diligence in these areas, pharmacists can significantly reduce the chances of errors and ensure safer medication practices.
The Critical Need for Precision in Medication Dosing
The stakes of precision in medication dosing are incredibly high for populations such as children and the elderly, who may be more susceptible to the effects of medication errors.
Potential Consequences of Inaccurate Dosing:
- Adverse Side Effects: Incorrect dosages can lead to complications, requiring additional medical interventions.
- Treatment Failures: Insufficient medication may prevent patients from receiving the desired therapeutic benefits, prolonging illness or worsening conditions.
Maintaining accuracy in unit conversions is a technical skill and a crucial aspect of responsible pharmacy practice.
Maintaining Accuracy in Unit Conversions
To ensure accuracy when converting between millilitres (mL) and ounces (oz), pharmacists should follow these guidelines:
- Complete calculations before rounding: Avoid premature rounding by finalizing all mathematical operations first.
- Use exact conversion factors: Always revert to the precise conversion of 29.5735 mL for 1 oz when calculating.
- Double-check work: Implement a verification process to catch potential errors before dispensing medications.
By adhering to these practices, pharmacists can achieve higher levels of precision in their dosage calculations.
Practical Experience in Rounding Conversions
Gaining practical experience in rounding conversions is invaluable for mastering this skill. Real-world applications can provide a deeper understanding of how these conversions impact patient care.
Opportunities for Practice:
- Internships: Gain hands-on experience in a hospital or retail pharmacy setting where rounding conversions are frequently used.
- Simulation Exercises: Participate in simulation training that mimics real-life pharmacy scenarios requiring quick and accurate calculations.
The more you practice, the more automatic these conversions will become, boosting your confidence during the NAPLEX and in your future career.
Real-World Applications of Rounding Techniques
Understanding how to round millilitres to ounces has significant implications in real-world pharmacy practice. For instance, consider a situation where a patient is prescribed a liquid medication requiring a dose of 15 mL.
The pharmacist must determine how many ounces to dispense. By applying the conversion factor, 15 mL is roughly 0.5 oz, which may be rounded to 0.5 oz for practical dispensing purposes. However, the importance of context must be considered.
In a pediatric setting, where dosages are often weight-based and meticulously calculated, rounding must be executed with heightened scrutiny to prevent underdosing or overdosing.
Each scenario demands understanding the specific patient population, the medication involved, and the potential consequences of rounding errors.
Strategies for Overcoming Rounding Challenges
Pharmacists often face challenges when rounding millilitres to ounces, mainly when working under pressure in fast-paced environments. One effective strategy is to develop a systematic approach to calculations.
For example, always write down the conversion factor, perform the calculation step-by-step, and only apply rounding at the end. Also, mnemonic devices can aid memory retention for commonly used conversion factors and rounding rules.
Practising these strategies in mock scenarios or with a study group can enhance confidence and reduce anxiety, ensuring that pharmacists are better prepared to handle real-life situations precisely.
The Ethical Responsibility of Accurate Dosing
Pharmacists carry a profound ethical responsibility to ensure that medications are dispensed accurately. This responsibility extends to every aspect of practice, including rounding.
Miscalculating a dose—even slightly—can lead to significant health consequences for patients. Ethical pharmacy practice involves adhering to established rounding protocols and advocating for patient safety by double-checking calculations and seeking clarification when needed.
Additionally, pharmacists must remain vigilant when working with new technologies or automated systems for measurement conversions in pharmacy, as reliance on technology should not replace the foundational skills necessary for manual calculations.
Collaborating with Healthcare Teams for Optimal Dosing
Effective collaboration with other healthcare professionals can significantly enhance the accuracy of medication dosing. Pharmacists play a crucial role in interprofessional teams, providing valuable input regarding drug formulations, dosing adjustments, and rounding considerations.
By communicating openly with physicians, nurses, and other team members, pharmacists can help ensure that the entire care team is aligned on medication management strategies. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of safety, as everyone involved can share insights and verify calculations, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Additionally, participating in team meetings focused on case studies can provide opportunities for pharmacists to discuss and refine their approaches to dosing protocols for pharmacists, enhancing their knowledge and practice.
The Role of Continuing Education in Medication Rounding
Continuing education is vital for pharmacy professionals, particularly concerning medication rounding techniques. The pharmacy field is ever-evolving, with new drugs, protocols, and technologies emerging regularly.
Engaging in ongoing professional development ensures that pharmacists remain current on best practices for calculating medication dosage. Many pharmacy schools and organizations offer workshops, online courses, and webinars on advanced pharmacy math and pharmaceutical calculations.
Participating in these educational opportunities reinforces existing knowledge and exposes pharmacists to new methodologies to enhance their ability to perform accurate conversions and improve patient safety.
Enhancing Skills with Technology and Study Guides

Various resources can enhance your skills in pharmaceutical calculations and rounding techniques. Utilizing study materials designed for the NAPLEX can reinforce your understanding and application of these concepts.
Recommended Study Resources:
- RxPrep: Comprehensive study guide that includes practice problems related to measurement conversions in pharmacy.
- Kaplan: Offers targeted practice for pharmaceutical calculations and NAPLEX study tips.
In addition to manual calculations, consider using apps and online tools that facilitate quick conversions. However, as you prepare for the exam, remember that reliance on technology may only sometimes be feasible, so developing your mental calculation skills is crucial.
Conclusion
Mastering the conversion of millilitres to ounces is essential for success in the NAPLEX 30, particularly in rounding. Understanding when and how to apply rounding rules can significantly impact dosing accuracy, which is vital for patient safety.
For instance, knowing that one ounce is approximately 29.57 mL allows for precise conversions, yet many pharmacists often simplify this to 30 mL per ounce for convenience. However, avoiding premature rounding during calculations is crucial to maintain accuracy.
Utilizing study resources like RxPrep or Kaplan can further enhance your skills, providing practice problems that simulate exam conditions.
Ultimately, mastering the nuances of rounding mL to oz is beneficial for passing the NAPLEX and critical for ensuring safe and effective pharmacy practice. Emphasizing precision in every conversion solidifies your competence as a future pharmacist.








